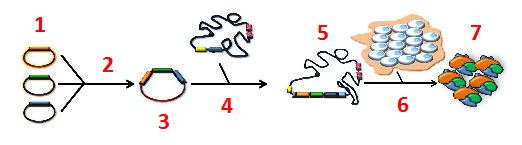
Traditional molecular biology technologies and even modern synthetic biology technologies do not allow for convenient modular assembly and disassembly of co-expression vectors for production of multiple proteins in a single eukaryotic cell. The MultiBac™ expression system uses DNA recombination to allow for easy, high-throughput compatible construction of baculovirus vectors for multiprotein expression in insect cells. Multiprotein coexpression is required to produce protein complexes, such as multivalent vaccines, or multiple individual proteins in the same cell, such as for signaling pathways. Multiexpression technologies are also the cornerstone of the emerging synthetic biology revolution. The MultiBac™ platform has been used for production of whole intact signal transduction pathways such as GPCR signaling cascades, kinase cascades, and protease cascades. MultiBac™ has also been used for production of virus like particles (VLPs) and a wide variety of multiprotein complexes. Baculovirus Expression Vector Systems (BEVS) such as MultiBac™ are a front line technology platform for production of protein kinases, GPCRs and ion channels for drug discovery, and are a major area of interest as delivery vectors for gene therapy. Insect cell expression using baculovirus as a vector is also becoming increasingly used in manufacturing of biopharmceuticals. MultiBac™ transfer vectors are fully synthetic, comprising only functional DNA, and as a result are small and easy to handle. The MultiBac™ baculovirus genome (DH10EMBacY) is under continuous development to remove harmful/non-essential genes (e.g. v-cath and chiA) and DNA recombination hotspots, and contains an integrated fluorescent protein expression cassette to allow for easy monitoring of virus titer. MultiBac™ is presently used by over 1000 academic and industrial laboratories around the world.
Click here to download MultiBac™ User Manual v9.0
Click here for DNA vector sequences
Click here to download MultiBac™ Short Description
Click here to download Cre-ACEMBLER User Manual 3.0
Click here to download Cre-ACEMBLER Short Description